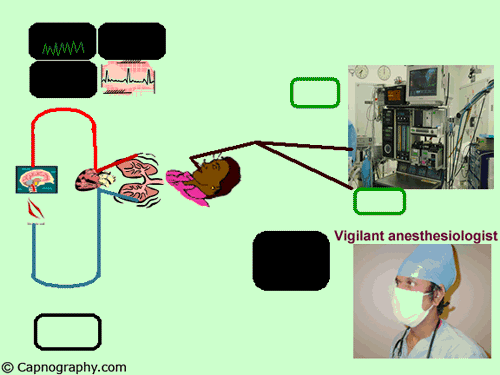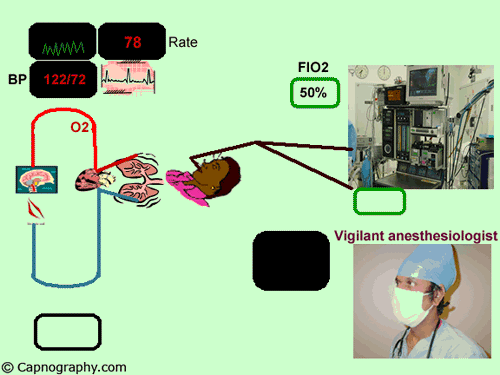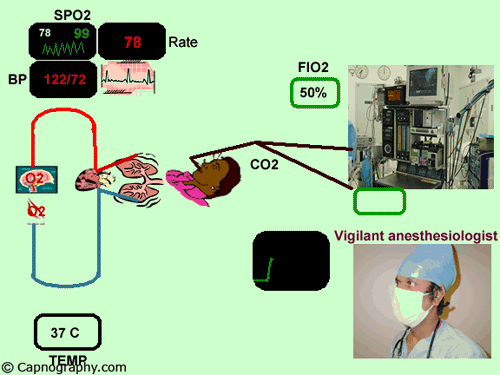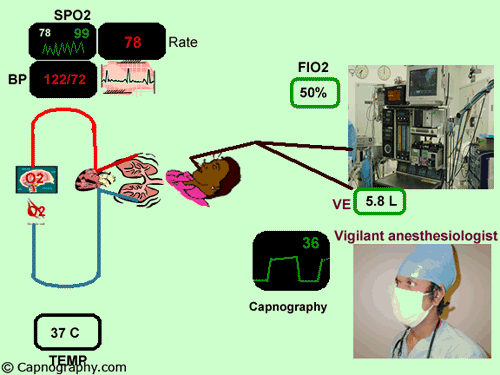
end-tidal co2 monitoring standard of care
End-tidal carbon dioxide detection is the most accurate technology to evaluate endotracheal tube posi-tion in patients who have adequate tissue perfusion. EtCO2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of CO2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the alveolar CO2 concentration.
End-tidal CO2 monitors can give healthcare providers an early warning if a patient is experiencing respiratory distress or going into respiratory failure.

. End-tidal CO2 monitoring allows for almost immediate information about what is going on with a patient. Implementation of Standard of monitoring resulted in a 66 reduction in malpractice insurance premiums over the period from 1986 to 1991. Noninvasive real-time CO 2 measurement can provide an early warning of impending hypoxaemia and the need for prompt intervention.
Allows trending of PaCO. In one year 1989 malpractice premium was cut by 33. What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2.
This practice however is not supported by well-controlled clinical trials. These standards stated Monitoring end-tidal C02 is an emerging standard and is strongly preferred What did the authors of these standards mean when they used the word emerging A subsequent discussion by Eichhorn et. Prospective cross-sectional comparative one-group pre-post design.
However the specific patient-safety orientation particularly the detection of inadequacy or overt failure of ventilation was seen as key point with the integral. Al 3 of how the-se standards were conceived gestated and delivered strongly suggests that they intended capnography to be a standard as soon as. Further the Committee acknowledged the fact that the end-tidal CO 2 numerical value displayed on a monitor during mask anesthesia often may be influenced by gas mixing in the patients airway and in the mask.
Despite the majority of literature being case series expert opinion would suggest. In the monitoring advisory bulletin May 2011 the AAGBI alerted their members about the fourth National Audit Project1The Intensive Care Society of United Kingdom also published a booklet 2011 titled Standards for Capnography in Critical Care Standards and GuidelinesThey made a strong recommendation to use capnography in all critically ill patients during the procedures. Properly placed endotracheal tubes may become displaced due to movement of patients andor equipment.
Use of heart rate electrocardiography noninvasive and arterial blood pressure atrial pressure pulse oximetry and end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in the pediatric critical care unit is commonplace. This observation is non-invasive and occurs through a gas sampling line attached to a mask or nasal prongs in the spontaneously breathing patient. 2 - a clinical estimate of the PaCO.
2 when ventilation and perfusion are appropriately matched Wide gradient is diagnostic of a ventilation -perfusion mismatch Use etCO. This was the direct proof of success of implementation of monitoring standards. 57 In addition a good correlation between arterial PCO 2 and end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 partial pressure has been observed during both mechanical ventilation and spontaneous breathing.
When capnography or capnometry is utilized the end tidal CO2 alarm shall be audible to the anesthesiologist or the anesthesia care team personnel When ventilation is controlled by a mechanical ventilator there shall be in continuous use a device that is capable of detecting disconnection of components of the breathing system. Waveform capnography should be monitored in all intubated patients and displayed on the monitor as above. At the end of expiration etCO.
8 However EtCO 2 monitoring is not currently standard. This eliminates the need to wait for blood work chest-x-rays and other diagnostic tests. To determine if end-tidal carbon dioxide etCO2 value increased nurses perceptions of confidence in patients readiness for postanesthesia care unit PACU discharge.
2 noninvasive measurement of CO. Carbon dioxide in the blood and end tidal capnography measures the partial pressure of carbon dioxide at the end of an exhaled breath. As a non-invasive trend even when there is a wide.
Continuous assessment of correct endotra-. The American Society of Anesthesiologists ASAStandards for Basic Anesthetic Monitoring updated in 2010 now states that the adequacy of ventilation during general anesthesia and moderatedeep sedation shall be continually evaluated by both qualitative clinical signs and monitoring of expired carbon dioxide. 10 This identifies the monitoring of expired carbon.
End tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2.

Shanghai Jaqi Medical Equipments Medical Hospital Furniture Medical Equipment

Cleo Etco2 Monitor With Vitals Infinium Medical

Capnography Vs Spo2 The Difference Could Be Life Changing

A Systematic Approach To Capnography Waveforms Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Defibrillator Monitor Automated External Defibrillator Monitor Gaming Products

Monitoring Ventilation With Capnography Nejm

Standard Six Paremater Icu Monitor Ibp And Etco2 Optional Medical Medical Equipment Icu

Pin On Smart Patient Monitor Device

Using Capnography To Titrate Cpap Ems Airway

Meditech Android Patient Monitor Md905 Md905 Monitor Vital Signs Monitors Patient